Currently, the detection methods of serum 25-OH-VD is mainly focused on Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and Chemiluminescence Immunoassay (CLIA). The national health industry standard WS/T 677-2020 recommends LC-MS/MS as the first screening method for vitamin D deficiency, and Chemiluminescence Immunoassay as the second screening method. These two methods have their own advantages and disadvantages in clinical detection. LC-MS/MS is a direct analysis method based on the molecular weight, structure and other chemical properties of the tested sample, and has high sensitivity and high specificity. CLIA is an immunoassay technology based on antigen-antibody specific binding. Compared with LC-MS/MS, it has simple pretreatments for samples and higher level of automation for detection.
Why LC-MS/MS is the ‘Gold Standard’
LC-MS/MS is the most preferred method for the detection of biochemical small molecules in clinical, which integrates the physical separation of liquid chromatography and the mass analysis of mass spectrometry. LC-MS/MS adopts two-stage tandem mass spectrometry analysis, which can utilize the information of precursor ions as well as fragment ions at the same time to selectively monitor the compounds to be quantified, and even trace components are not interfered by abundant substances. For the analysis and detection of small molecules like 25-OH-VD, LC-MS/MS has relatively high analytical specificity and detection sensitivity.
Limitations in clinical applications
LC-MS/MS is easily affected by substances other than the target small molecules in the samples to be tested. These interfering substances include endogenous substances from the sample itself and the external substances introduced from the environment during the method establishing process. In order to eliminate this matrix effect and improve the accuracy of LC-MS/MS analysis results, the samples have to be strictly pre-treated. Inspectors need to select appropriate sample pretreatment methods according to matrix purification effect, expected sample concentration, minimum detection limit and other factors to eliminate matrix effects caused by different substances.
Limitations of CLIA Competition Method in Clinical Applications
Poor consistency with LC-MS/MS detection results
At present, for small molecules with low molecular weight and insufficient antigenic epitopes like 25-OH-VD, the CLIA competition method is most commonly used immunoassay in clinical detection. Plenty of studies have revealed that the CLIA competition method has poor correlation with LC-MS/MS in detection results.
Researchers from the Laboratory Department of Peking Union Medical College Hospital of Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and the China-Japan Friendship Hospital compared the 25-OH-VD detection reagents of five major brands (Abbott, DiaSorin, IDS, Roche, Siemens) on the market and found that in these reagents, the coincidence rate between the test results and the clinical judgments based on LC-MS/MS test results was less than 71% (Table 1).
Table 1. Consistency between clinical judgments of LC-MS/MS and different CLIA competition methods
| Supplier | All Samples (245 cases) | |||
| <20ng/mL N(%) |
20~30ng/mL N(%) |
>30ng/mL N(%) |
Coincidence Rate |
|
| LC-MS/MS | 99(40.4) | 68(27.8) | 77(31.4) | — |
| A | 115(46.9) | 79(32.3) | 51(20.8) | 68.60% |
| B | 127(51.8) | 94(38.4) | 24(9.8) | 64.90% |
| C | 95(38.8) | 104(42.4) | 46(18.8) | 67.80% |
| D | 121(49.4) | 79(32.2) | 45(18.4) | 70.60% |
| E | 39(15.9) | 72(29.4) | 134(54.7) | 51.80% |
Note: A, B, C, D, and E represent Abbott, DiaSorin, IDS, Roche, and Siemens in order. Among them, Abbott, IDS and Siemens use the AE Chemiluminescence competition method, DiaSorin uses the Isoluminol derivatives direct Chemiluminescence competition method, and Roche uses the Electrochemiluminescence competition method.
Poor recognition of 25-OH-VD2
The study above also found that no matter what kind of CLIA system, when the sample contains 25-OH-VD2, the correlation between the competition method and the LC-MS/MS decreases in detection results. It can be concluded that the major detection reagents circulating on the market for CLIA competition method do not recognize 25-OH-VD2 well, which directly affects the consistency of the reagents and LC-MS/MS detection results (Table 2).
Table 2. 25-OH-VD2 content vs. its Impacts to CLIA competition test results
| Sample | Slope | 95% CI | Intercept | 95% CI | r Value | 95% CI | Deviation | 95% CI | Deviation% | 95% CI |
| Without 25-OH-VD2 (154 cases) | ||||||||||
| A | 0.96 | 0.90~1.01 | 2.05 | 1.16~3.19 | 0.917 | 0.887~0.939 | 1.0 | 0.3~1.7 | 8.6 | 4.9~12.3 |
| B | 0.83 | 0.79~0.88 | 1.61 | 0.92~2.21 | 0.930 | 0.905~0.948 | -2.5 | -3.2~-1.8 | -8.7 | -11.9~-5.5 |
| C | 0.68 | 0.63~0.73 | 8.83 | 7.80~9.97 | 0.885 | 0.845~0.915 | 1.7 | 0.8~2.7 | 18.2 | 13.0~23.4 |
| D | 0.95 | 0.89~1.02 | 1.08 | -0.07~2.02 | 0.909 | 0.877~0.933 | -0.5 | -1.3~0.3 | -1.2 | -5.0~2.6 |
| E | 1.29 | 1.17~1.42 | 5.34 | 2.94~7.47 | 0.848 | 0.796~0.887 | 10.8 | 9.5~12.1 | 44.7 | 39.8~49.7 |
| Contain 25-OH-VD2 (91 cases) | ||||||||||
| A | 0.66 | 0.56~0.75 | 4.41 | 1.80~6.92 | 0.804 | 0.717~0.867 | -5.3 | -6.5~-4.1 | -19.9 | -24.8~15.0 |
| B | 0.78 | 0.70~0.87 | -0.4 | -2.63~1.68 | 0.854 | 0.787~0.902 | -6.8 | -7.8~-5.7 | -30.1 | -34.2~26.0 |
| C | 0.77 | 0.68~0.86 | 2.51 | 0.05~4.61 | 0.845 | 0.773~0.895 | -3.8 | -4.8~-2.7 | -14.0 | -18.4~-9.7 |
| D | 1.03 | 0.90~1.17 | -5.48 | -9.10~-2.51 | 0.819 | 0.738~0.877 | -5.0 | -6.2~-3.8 | -25.0 | -30.2~-19.7 |
| E | 1.47 | 1.16~1.92 | -1.70 | -13.59~5.86 | 0.626 | 0.482~0.737 | 11.3 | 8.7~13.8 | 33.8 | 27.5~40.1 |
| Total Samples(245 cases) | ||||||||||
| A | 0.85 | 0.78~0.91 | 2. 84 | 1.68~3.80 | 0.848 | 0.808~0.880 | -1.3 | -2.1~-0.6 | -2 | -5.4~1.4 |
| B | 0.78 | 0.73~0.82 | 1.58 | 0.77~2.31 | 0.894 | 0.866~0.920 | -4.1 | -4.7~-3.5 | -16.6 | -19.4~-13.8 |
| C | 0.67 | 0.62~0.72 | 7.54 | 6.38 ~8.44 | 0.841 | 0.800~0.874 | -0.3 | -1.1~0.5 | 6.2 | 2.1~10.4 |
| D | 0.93 | 0.87~1.00 | -0.31 | -1.43~0.61 | 0.866 | 0.831~0.894 | -2.2 | -2.9~-1.5 | -10.0 | -13.4~-6.6 |
| E | 1.30 | 1.18~1.43 | 4.04 | 1.81~6.44 | 0.776 | 0.721~0.822 | 11.0 | 9.7~12.2 | 40.7 | 36.7~44.6 |
Note: The data in Table 2 are results comparing with LC-MS/MS.
Most of the binding sites between small molecules and corresponding antibodies are cave-like structures, and majority of the structure of small molecules is covered, resulting in insufficient antibody binding space. Thus, traditional sandwich immunoassay techniques are difficult to detect small molecules. In order to break through the technical barriers of sandwich antibodies for small molecules, the R&D team of OKayBio continued to practice and kept challenging, and finally successfully developed antibodies and bulk packs of reagents suitable for 25-OH-VD sandwich immunoassays by adjusting the immune strategies and optimizing antibody designs.
It has been verified that the 25-OH-VD sandwich antibodies of OKayBio have strong abilities to recognize the total 25-OH-VD. The bulk packed reagents were inspected on the AE Chemiluminescence platform. The correlation (R2) between the self-test results and the mass spectrometry results was 0.9153, and the correlation (R2) between the customer-verified results and the mass spectrometry results was up to 0.945.
Self-tested sample coincidence rate
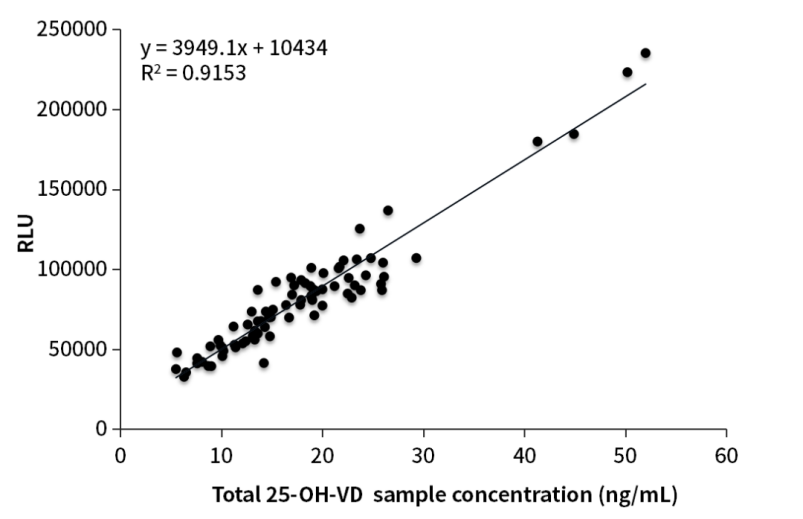
Figure 1. Clinical comparative analysis
(Sandwich-MS assigned)
In order to improve the accuracy of 25-OH-VD immunoassay results, the production of OKayTM bulk packed reagents (Q80h1) for Chemiluminescent sandwich method benchmark the industrial ‘Gold Standard’ for detection - LC-MS/MS. Verified by the AE Chemiluminescence platform, the Q80h1 detection results were in good consistency with the mass spectrometry detection results, and the correlation (R2) can reach 0.9153 (Figure 1). In conclusion, the sandwich method improved the accuracy of the immunoassay results effectively.
Customer-verified sample coincidence rate
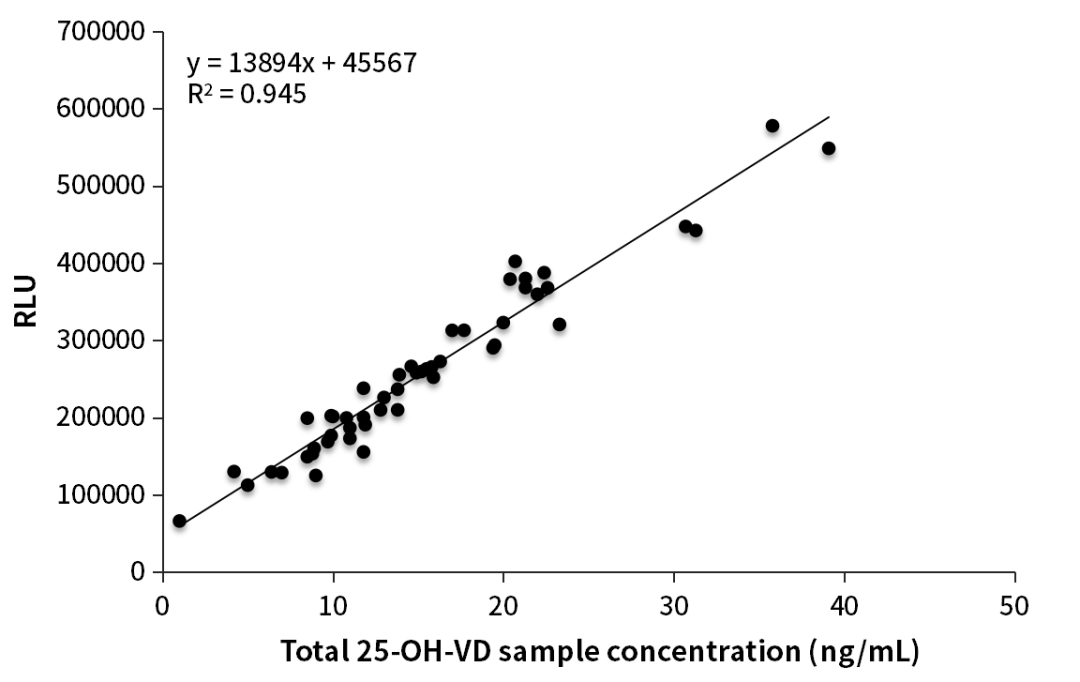
Figure 2. Clinical comparative analysis
(Sandwich-MS assigned)
Our customer used OKayTM Q80h1 to test the mass spectrometry assigned samples, the preliminary test results were in good consistency with the mass spectrometry test results, and the correlation (R2) was up to 0.945 (Figure 2).
Total 25-OH-VD recognition capacity
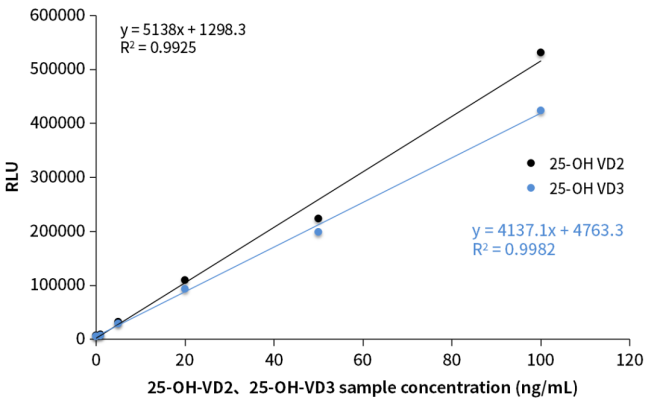
Figure 3. Recognition capacity of sandwich antibody to total 25-OH-VD
Studies from the Laboratory Department of Peking Union Medical College Hospital of Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and the China-Japan Friendship Hospital revealed that the cross-reactivity between 25-OH-VD antibody and 25-OH-VD2 directly affects the accuracy of total 25-OH-VD detection results. Verified by the Chemiluminescence platform, OKayTM 25-OH-VD sandwich antibodies have good cross-reactivity with 25-OH-VD2 and 25-OH-VD3, and can effectively identify the total 25-OH-VD in the sample.
The successful development of 25-OH-VD sandwich antibodies marked the first step of ‘technique innovation for small molecule sandwich antibody’ by Nanjing OKayBio. The 25-OH-VD sandwich antibodies not only have good consistency with the ‘Gold Standard’ test results of mass spectrometry, but also makes up for the limitations of the CLIA competition method in clinical detection to some extent. In the future, OKayBio will continue to launch more high-quality detection projects for small molecules.
| Hypertension | AⅠ, AⅡ, ALD |
| Thyroid | T3, T4 |
| Gestation | Prog, E2 |
| Anemia | FA, VB12 |
25-OH-VD Antibody
| Method | Catalog # | Label | Recommended use | Recommended pair | Platform |
| Sandwich | L216u1 | AE | Detection | L216u1-L217u1 | Chemiluminescence |
| L217u1 | Biotin | Capture | |||
| R483k3 | - | Detection | R483k3-R484j4 | ||
| R484j4 | - | Capture | |||
| R485m5 | - | Detection | R485m5-R486n6 | ||
| R486n6 | - | Capture | |||
| Competition | K32w6 | - | Detection | - | Chemiluminescence, Immunochromatography, Turbidimetric Immunoassay |
| L210u1 | AE | - | - | ||
| L212u1 | ALP | - | - | ||
| L219u1 | Biotin | - | - |
25-OH-VD Antigen
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Conjugate |
| Antigen | C1580 | Synthesized | BSA |
Miscellaneous
| Name | Catalog # | Recommended Dosage | Platform |
| Dissociation Agent | D10a1 | 50μL /sample | AE/ALP Chemiluminescence |
Nanjing OKay Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (briefly referred as Nanjing OKayBio) is a total solution provider of in vitro diagnostic raw materials, and has been committed to the rapid development and large-scale production of proteins and antibodies for in vitro diagnostics. Nanjing OKayBio insists on independent innovation and constantly breaking through key technologies. Nanjing OKayBio owns Protein structure analysis platforms, Flow-Cytometry platforms, Hybridoma platforms, and Single-cell sequencing platform to support continuous iterations in products. Nanjing OKayBio has passed the ISO 9001/ ISO 13485 quality system double certification and insist on continuous optimization. Combined with self-built Immunochromatography platform, Turbidimetric Immunoassay platform, Chemiluminescence platform and Fluorescence-activated cell sorting Flow-Cytometry platform, the quality stability of our products is effectively controlled no matter in the production process or at the final delivery stage. Nanjing OKayBio also owns SingleB? rapid monoclonal antibody discovery platform, BGE? high-throughput expression platform, DeepLight? functional pre-screening platform and macromolecule purification platform, which provide a strong guarantee for our product performance and product quality.
References
[1]? Makris K, Bhattoa HP, Cavalier E, Phinney K, Sempos CT, Ulmer CZ, Vasikaran SD, Vesper H, Heijboer AC. Recommendations on the measurement and the clinical use of vitamin D metabolites and vitamin D binding protein - A position paper from the IFCC Committee on bone metabolism. Clin Chim Acta. 2021 Jun;517:171-197.
[2]Beccaria M , Cabooter D . Current developments in LC-MS for pharmaceutical analysis. Analyst. 2020 Feb 17;145(4):1129-1157.
[3] Grebe SK, Singh RJ. LC-MS/MS in the Clinical Laboratory - Where to From Here? Clin Biochem Rev. 2011 Feb;32(1):5-31.
[4]?Han S, Qiu W, Zhang J, Bai Z, Tong X. Development of a Chemiluminescence Immunoassay for Quantification of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D in Human Serum. J Anal Methods Chem. 2020 Aug 1;2020:9039270.?
